Abstract
Allogeneic stem cell transplantation (alloSCT) is a curative treatment for patients with hematological malignancies. The anti-tumor or Graft-versus-Leukemia (GvL) effect of alloSCT is mediated by donor T cells targeting patient hematopoietic cells. Donor T cells may, however, also target non-hematopoietic tissues of the patient, thereby inducing Graft-versus-Host Disease (GvHD). Patients without suitable related donors are transplanted with unrelated donors matched for HLA-A, -B, -C, -DRB1, and -DQB1 (10/10 match). HLA-DP alleles are mismatched in most patients transplanted with unrelated donors. HLA class II molecules are mainly expressed on hematopoietic cells, but under inflammatory conditions the expression of HLA class II on non-hematopoietic tissues is upregulated, thereby increasing the risk of GvHD. To reduce this risk and retain the anti-tumor effect, patients transplanted with unrelated donors may be treated with immunotherapy specifically targeting hematopoietic peptides presented by mismatched HLA-DP. CD45 is an attractive source protein for these peptides because of its broad expression in all hematopoietic lineages. Despite CD45 expression, healthy hematopoietic cells after alloSCT are of donor origin and will therefore be spared.
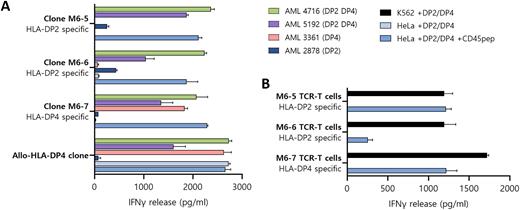
To investigate whether CD45 peptides are presented by HLA-DP on hematopoietic cells, peptides were eluted from HLA-DP and measured by tandem mass spectrometry. HLA-DP peptidome data were generated from acute myeloid leukemia (AML) cases as well as hematopoietic (CD45pos) K562 cells separately transduced with 13 different HLA-DP alleles. Peptidome searching revealed one CD45 peptide on K562 cells transduced with HLA-DP2 (DPA1*01:03 & DPB1*02:01) or HLA-DP4 (DPA1*01:03 & DPB1*04:01 or DPB1*04:02) as well as AML cases expressing these HLA-DP alleles. Next, (CD45pos) K562 cells transduced with HLA-DP2 or HLA-DP4 and costimulatory molecules (CD40, CD80, CD86) were used to stimulate CD4 T cells from healthy individuals negative for these HLA-DP alleles. After 14 days of stimulation, CD4 T cells were restimulated and activated CD137+ and CD154+ CD4 T cells were single cell sorted. Growing T cell clones were screened for reactivity against CD45 peptide loaded on non-hematopoietic (CD45neg) HeLa cells transduced with HLA-DP2 or HLA-DP4. Three clones were able to specifically recognize CD45 in HLA-DP2 or HLA-DP4 (Figure 1A). T cell clones M6-5 and M6-6 were specific for CD45 in HLA-DP2, and clone M6-7 recognized the CD45 peptide in HLA-DP4. No cross-reactivity was observed against other HLA-DP alleles. In addition to HLA-DP transduced K562 cells, all T cell clones specifically reacted against HLA-DP2 or HLA-DP4 positive AML cases.
We next investigated whether the T cell receptors (TCRs) of the T cell clones could be used to engineer and redirect CD4 T cells to CD45-derived peptides in mismatched HLA-DP. The HLA-DP2 restricted TCRs of M6-5 and M6-6 and HLA-DP4 restricted TCR of M6-7 were sequenced, cloned and transferred to CD4 T cells from three HLA-DP2 and HLA-DP4 negative healthy donors. TCR-T cells showed specific reactivity against K562 transduced with HLA-DP2 or HLA-DP4, whereas HeLa cells with these HLA-DP alleles were not recognized (Figure 1B, example of one donor).
In conclusion, we identified three TCRs for a CD45 peptide presented by HLA-DP2 or HLA-DP4 that are able to target hematopoietic cells. The TCRs can be used for CD4 T cell immunotherapy to treat patients with hematological malignancies after HLA-DP mismatched alloSCT.
Figure 1. CD45 as a target for specific CD4 T cells. (A) CD4 T cell clones recognizing CD45 in HLA-DP2 or HLA-DP4 on AML. (B) M6-5, M6-6 and M6-7-TCR transduced CD4 T cells recognize HLA-DP2 or -DP4 transduced K562 (CD45pos) but not HeLa (CD45neg) cells.
Disclosures
Griffioen:Miltenyi Biotec B.V & Co. KG: Research Funding.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.

This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal